Today we’ll be using Make (formerly Integromat) in conjunction with monday.com to demonstrate the powers of cursor-based pagination!
When dealing with APIs for data retrieval, efficiently managing large datasets is crucial. Cursor-based pagination is a powerful method to query and navigate through these datasets. This blog post explores how to implement cursor-based pagination with the monday.com API via Make.com, a platform that connects apps and services with powerful automations.
Understanding Cursor-based Pagination
Cursor-based pagination involves using a pointer (cursor) to fetch a subset of data from a database or an API. Unlike traditional pagination that uses page numbers, cursor-based pagination provides a more efficient and reliable way to paginate through large datasets, especially in real-time environments where data is constantly changing.
Use Cases:
- Real-time Data Syncing: Ideal for applications requiring up-to-date information from monday.com boards.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Efficiently fetch large volumes of data for analytics and report generation.
- Integrations and Automations: Streamline workflows by integrating monday.com data with other services via Make.com.
Benefits:
- Improved Performance: Reduces load times by fetching smaller data chunks.
- Consistency: Offers stable navigation through data, even with real-time changes.
- Scalability: Handles large datasets effectively, crucial for enterprise-level applications.
Step-by-Step Implementation Example:
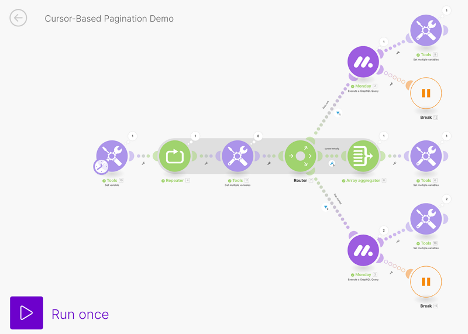
Here is the scenario: Imagine you’re building an automation to sync project tasks from a monday.com board to a Google Sheets spreadsheet. The goal is to fetch all tasks without missing any updates, using cursor-based pagination.
Prerequisites:
- An active monday.com account with access to API credentials.
- A Make.com account set up and ready to use.
- Basic familiarity with Make.com’s interface and monday.com’s API.
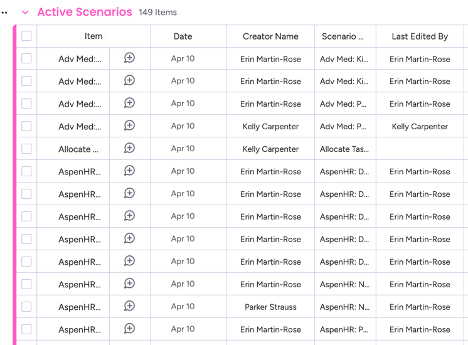
For an example I’ll be using this monday board with 149 items total. I want to only grab the items ‘Last Edited By’ myself, Erin Martin-Rose. There are 72 items total. First, we will make an API call to filter out those items, and then we’ll use cursor-based pagination to retrieve them all.
Here are the following steps, to ensure proper implementation:
- Set Up Your monday.com Integration on Make.com
- Navigate to Make.com and create a new scenario.
- Add monday.com as a service and authenticate your account.
- Create an example board with several items or apply this to an existing board.
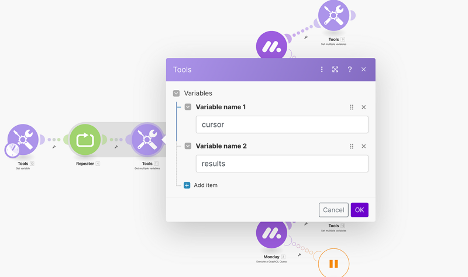
- Use the tools module, ‘Set a variable’ with an empty array as its value.
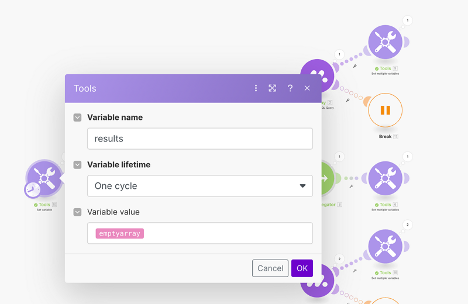
- This module provides a place to store the results for the subsequent iterations.
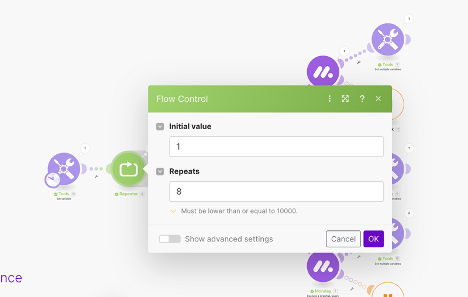
- Set up a Repeater module.
- Depending on how large your dataset is, you will input the number of repetitions accordingly. I’ve set my Repeater to 8, as I anticipate around 100 items returned. In my pagination modules I’m going to set the item limit to 25, so 8 iterations will be more than enough to retrieve all of the items.
- Add a ‘Get Multiple Variables’ module.
- Here we will retrieve the results array, as well as the cursor variable. We will set the cursor variable in subsequent modules. This module serves to append the new set of items to the results array for each iteration. We get the cursor variables value for each iteration, to determine when the cursor is empty. If the cursor is empty, the loop will end since we have retrieved all of the items.
- Add a Router.
- The router enables us to use alternative pathways in our scenario and gives us the opportunity to execute a path dependent on a set of conditions. You’ll find this module in the built-in Flow Controls modules.
- We will set up 3 routes: one for calling the items page, one for calling the next items page, and one for checking if the cursor is empty (if we’ve retrieved all items).
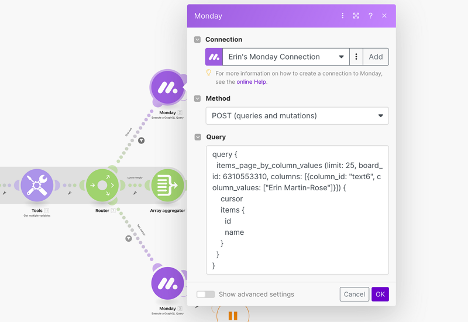
- Configure the monday.com ‘Execute a GraphQL Query’ Module
- Choose the ‘Execute a GraphQL Query’ module from monday.com’s options. We will be using the ‘items_page_by_column_values’ query. You can find an example of this query in monday’s GraphQL documentation. Simply follow this link and copy/paste the example or you can use the code example below. Be sure to replace the example data with your own relevant fields.Here is the link to monday’s API Docs:monday’s API Docs — items_by_column_values
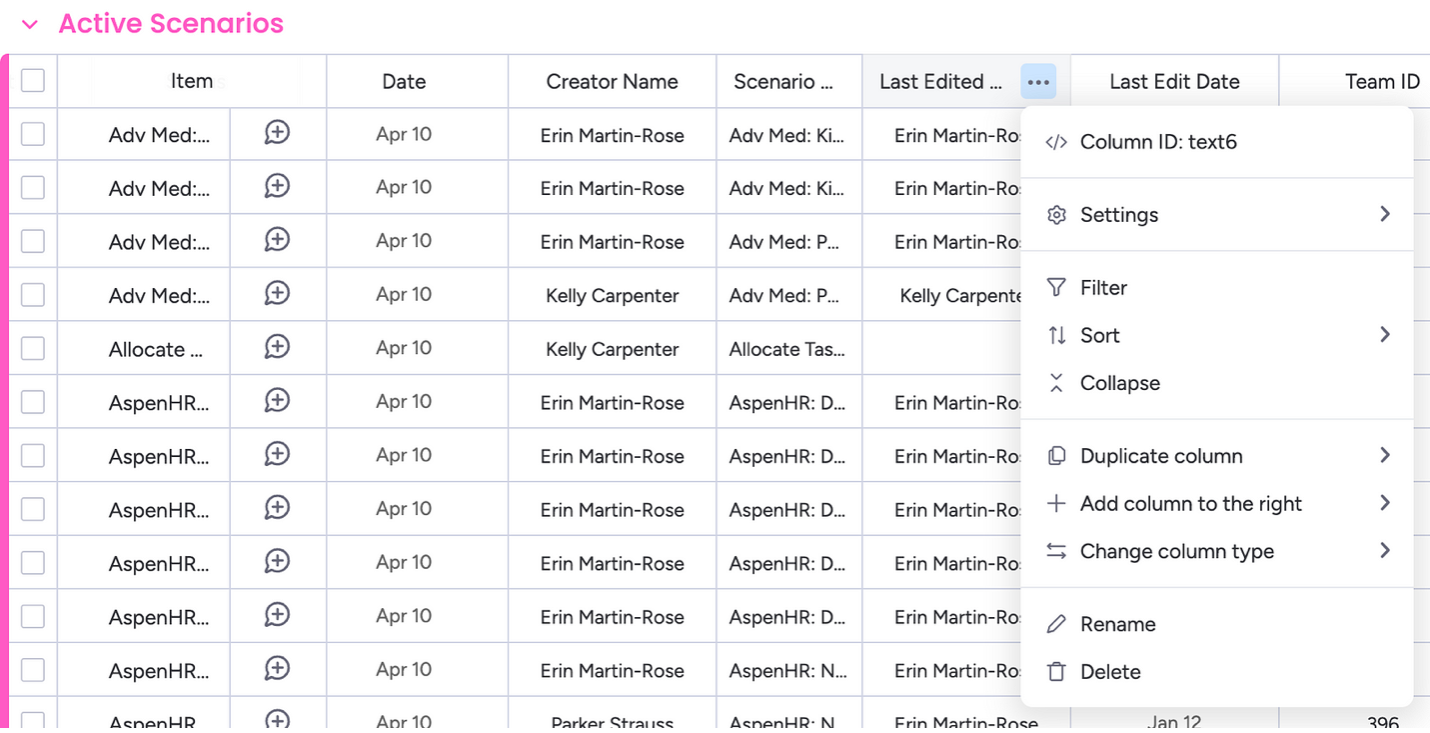
- Specify the board ID, column ID and the desired column value.
- You can find the column ID in your monday board as shown below.
Below is an example you can use to assist in creating your query:
query {
items_page_by_column_values (limit: 50, board_id: 6310553310, columns: [{column_id: “text6”, column_values: [“Erin Martin-Rose”]}]) {
cursor
items {
id
name
}
}
}
- Implement Cursor Logic
- Initially, the cursor will be empty. Fetch the first set of data by clicking ‘Run once’.
- We will use our loop to continue fetching data until no new cursor is returned, indicating you’ve retrieved all available data. In this example I’ve used the Repeater module to continue fetching our items until the loop is finished.
- Use filters to specify routes.
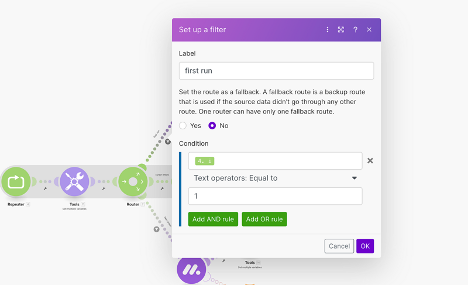
- Here we are adding a filter to ensure this route only executes once. Since this is the initial API call to retrieve our first page of items, we only want this route to execute once.
- Use variables to store iterated data.
- We will set a variable to continuously push data into our results array, and a variable to store the iteration’s associated cursor. The idea is that for each iteration — the data is pushed, and the cursor changes its point.
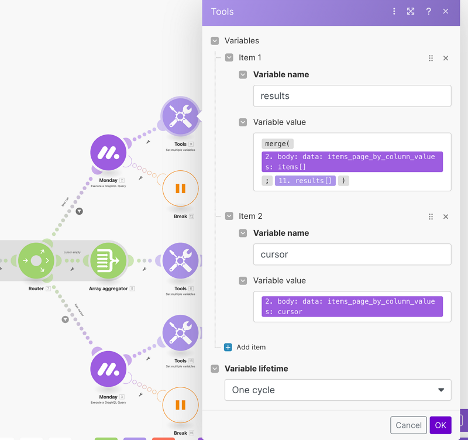
- With our first variable we use the merge() function to merge the two arrays — the array of items returned by our query, and the results array.
- The cursor is where we store our current cursor (the point where our last iteration left off).
- Use a fallback route to check if the loop is complete.

- Be sure to check the ‘Yes’ option in this filter. As described above, this route will only execute if all other routes fail. This will only execute once our iterations are finished.
- Use an ‘Array Aggregator’ to close the loop.

- The Array Aggregator enables us to stop the loop. Here I’m aggregating the number of iterations. This will give me a better idea of how many iterations I require specific to this dataset.
- I then use another tools module — ‘Set a Variable’ to store the output.
- Utilize a filter to check if the cursor still exists.
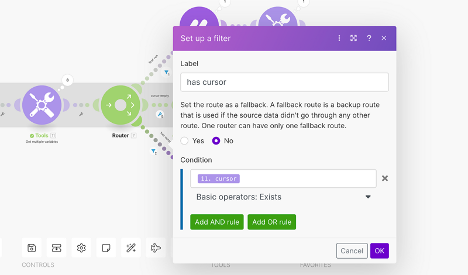
- This route will execute as many times as needed, until our cursor is empty. Once our cursor is empty, this signifies that we have retrieved all of the items.
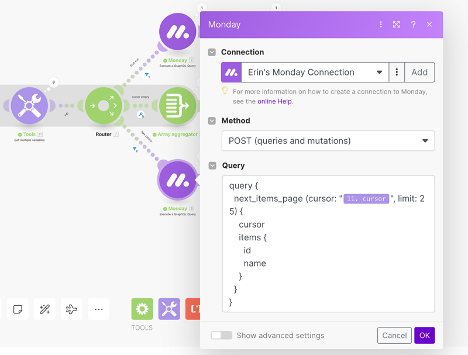
- Use the ‘Execute a GraphQL Query’ module to call on our next page of items.
- This module queries the API for the next page of items.
- The cursor represents where we left off according to our last call.
- By passing in the ‘cursor’ variable, we ensure that its value will change with each iteration.
- Merging results to mark completion.

- Here we are using setting the ‘cursor’ and ‘results’ modules to align with the next item’s page.
- Once one iteration is complete, the cursor will reset.
- We merge the output’s array with the results array. The output will continue to push into the results array until our loop is complete.
- See final results:

- As expected, the execution returned 72 items, and the loop ended once we retrieved all of our items.
In conclusion, Implementing cursor-based pagination with the monday.com API via Make.com offers a robust solution for managing large datasets and ensuring data integrity across applications. This approach not only enhances performance but also provides a scalable and reliable method for data retrieval and synchronization. In our example we only grabbed 72 items, but say you have a board with 5,000 items! This is where cursor-based pagination really shows its value.
As you build and refine your integrations, consider the benefits of cursor-based pagination for your next project.
Additional Resources

About the Author
Erin Martin-Rose, is a Business Automation Specialist at Axanexa, her expertise lies in harnessing the capabilities of platforms like monday.com and the automation tool Make.com. With her background in coding and a customer-centric approach, She creates dynamic workflows that not only enhance but truly transform operational performance, making work more efficient and user-friendly for everyone involved.
Partners:





